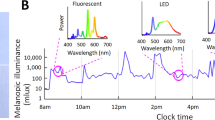
Abstract
Life in industrialized societies is primarily life inside buildings. Illumination from electric lighting in the built environment is quite different from solar radiation in intensity, spectral content, and timing during the 24-hour daily period. Humans evolved over millions of years with the day–night pattern of solar radiation as the primary circadian cue. This pattern maintained a 24-hour rhythm of melatonin release, as well as a host of other physiological rhythms including the sleep–wake cycle. Electric lighting in the built environment is generally more than sufficient for visual performance, but may be inappropriate for the maintenance of normal neuroendocrine rhythms in humans; e.g., insufficient during the day and too much at night. Lighting standards and engineering stress visual performance, whereas circadian function is not currently emphasized. The molecular biological research on the circadian clock and on mechanisms of phototransduction makes it clear that light for vision and light for circadian function are not identical systems. In particular, if electric lighting as currently employed contributes to `circadian disruption' it may be an important cause of `endocrine disruption' and thereby contribute to a high risk of breast cancer in industrialized societies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, R.G., Rea, M.S. Light in the Built Environment: Potential role of Circadian Disruption in Endocrine Disruption and Breast Cancer. Cancer Causes Control 12, 279–287 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011237000609
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011237000609