Abstract
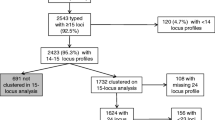
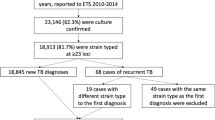
A 2-year, population-based, molecular epidemiological study was conducted in Milan, Italy, to determine the proportion of tuberculosis (TB) cases attributable to recent transmission. All strains were typed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis; clustering was considered indicative of recent transmission. Of the 581 cases, 239 (41.1%) belonged to clusters that consisted of 2 to 11 patients; 28.1% were attributable to recent transmission (number of clustered patients minus 1). Clustering was associated with multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains (74.2% of cases), AIDS (60.2%), and a history of incarceration (67.4%). The frequency of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis was 5.3% overall (15.4% among AIDS patients). Among AIDS patients, infection with a resistant strain was independently associated with clustering (odds ratio, 1.32; 95% confidence interval, 1.07–1.163), while among non-AIDS patients, three factors were associated with clustering: history of incarceration (odds ratio, 2.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.41–2.92), age <30 years (odds ratio, 1.43; 95% confidence interval, 1.05–1.94), and native-born Italian nationality (odds ratio, 1.44; 95% confidence interval, 1.08–1.92). Of the 118 patients who belonged to either the smallest or the largest cluster, 19 (16.1%) reported an epidemiological link with another study patient. The results of this study highlight the need for control programs that focus on selected high-risk groups consisting primarily of HIV-infected individuals and persons with social and lifestyle risks for TB. These programs should be aimed at reducing the probability of transmission of drug-resistant TB through early identification of cases and provision of effective treatment until the individual is cured.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moro, M., Salamina, G., Gori, A. et al. Two-Year Population-Based Molecular Epidemiological Study of Tuberculosis Transmission in the Metropolitan Area of Milan, Italy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 21, 114–122 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-001-0664-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-001-0664-2